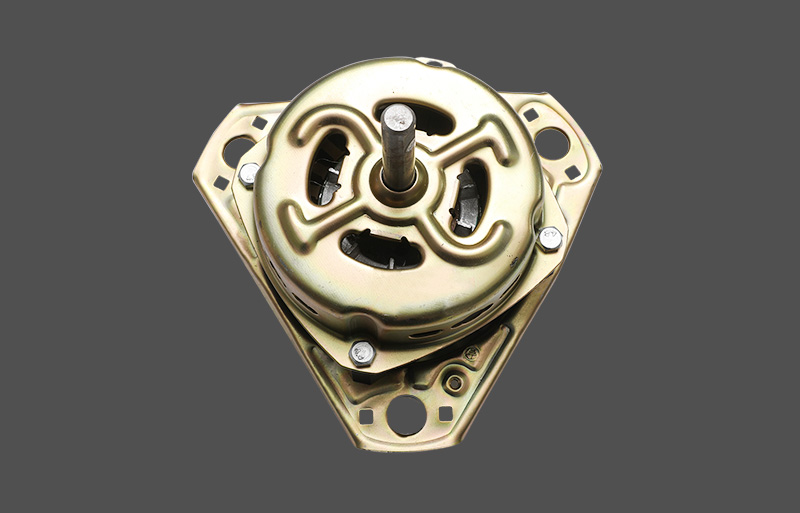
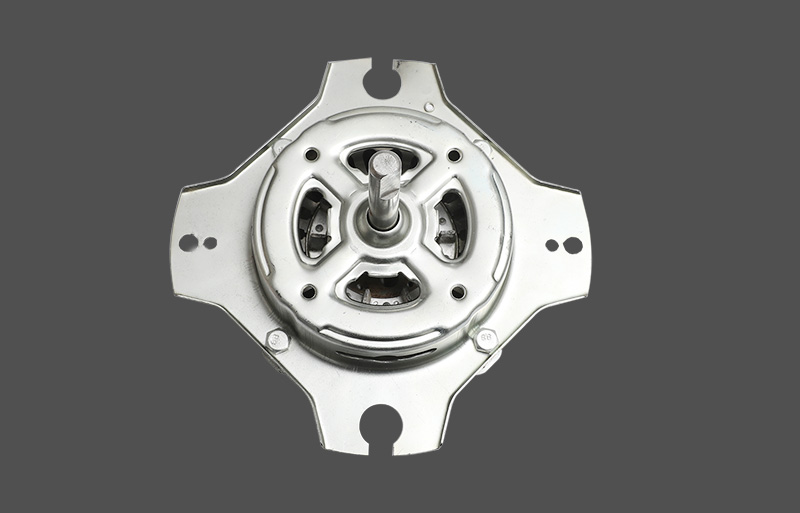
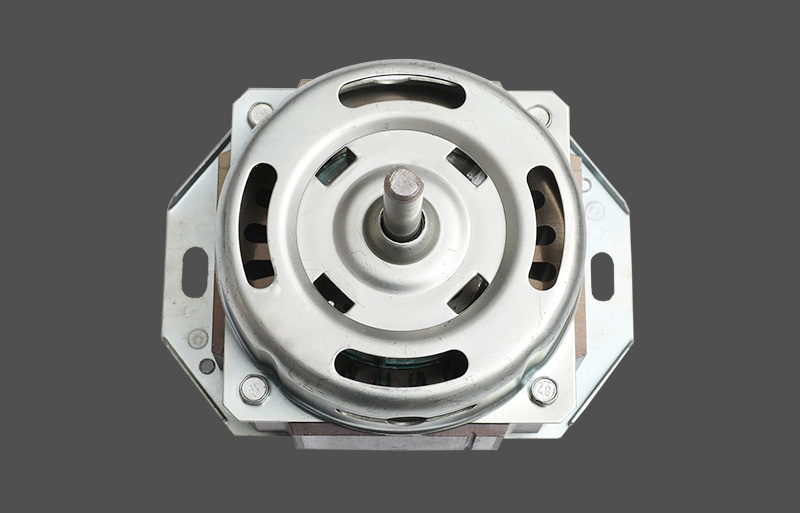
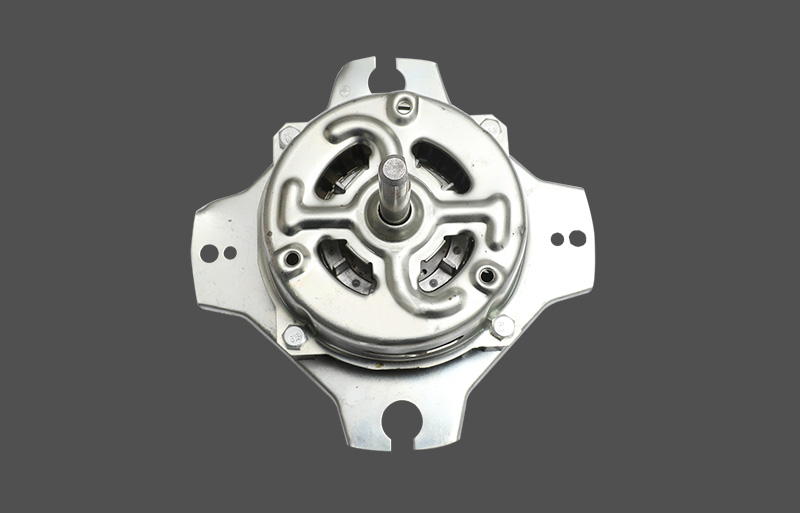
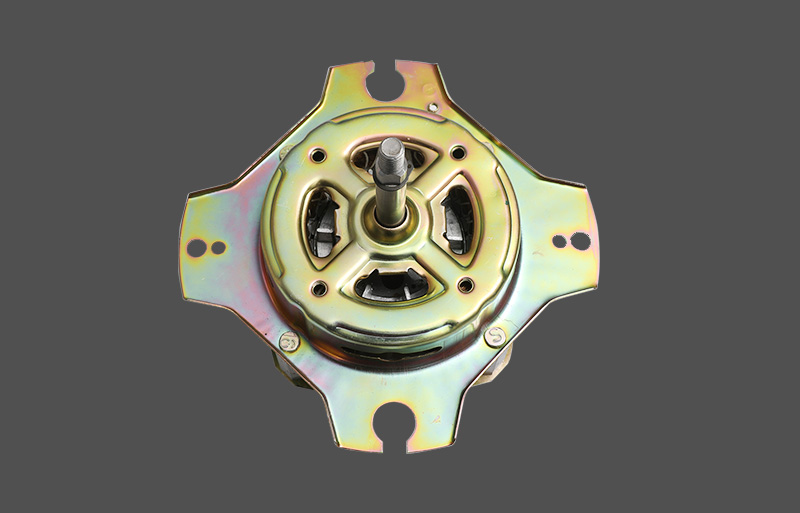
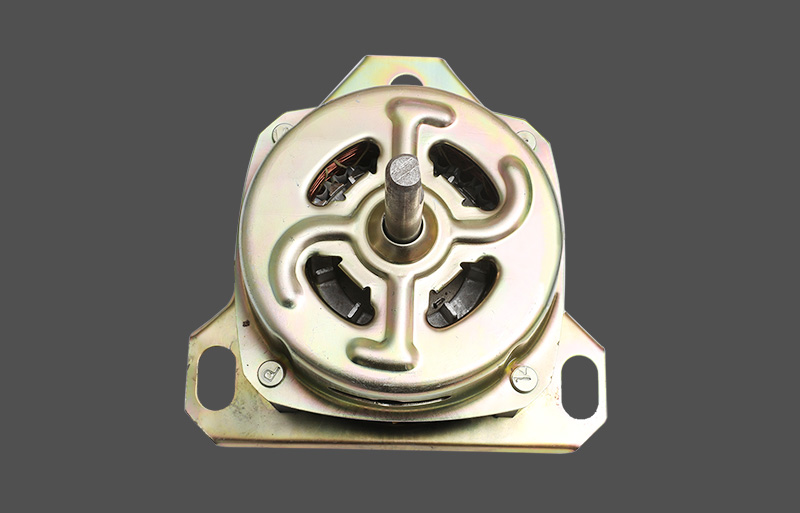
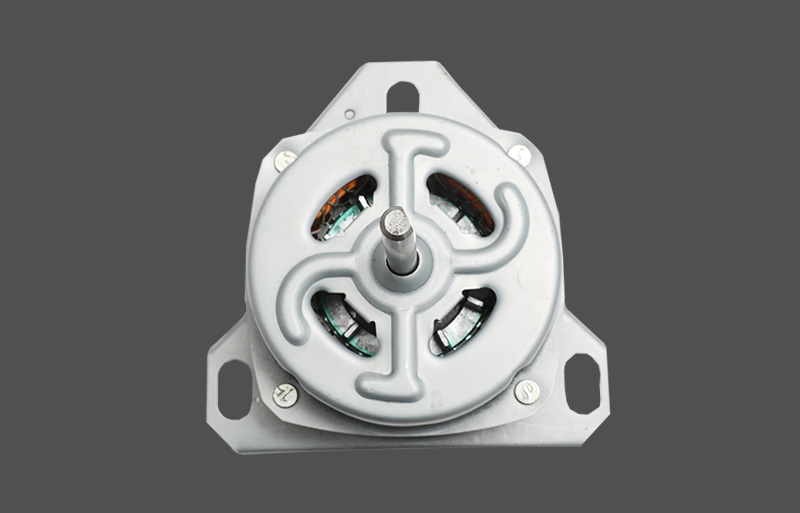
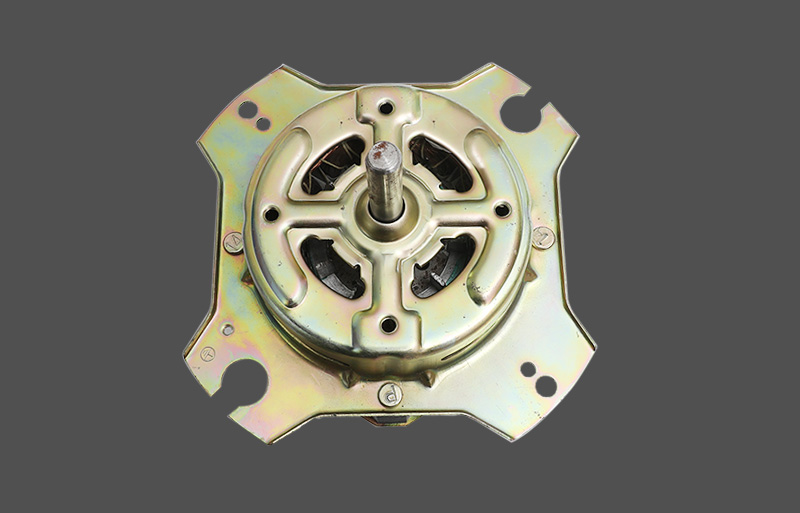
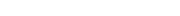Tá an mótair lucht leanúna ina seasamh is croí-chomhpháirt de lucht leanúna tí agus tráchtála araon. Le linn oibríochta, féadfaidh sé taithí a fháil ar róthéamh, rud a d'fhéadfadh tionchar a bheith aige ar shaolré an mhótair agus ar shábháilteacht oibriúcháin. Tá meicníocht cosanta teirmeach dea-dheartha riachtanach le haghaidh feidhmíocht chobhsaí agus marthanacht. Tugann an t-alt seo forbhreathnú gairmiúil ar na prionsabail dearaidh, na cineálacha, na meicníochtaí agus na feidhmeanna a bhaineann le cosaint theirmeach i mótair lucht leanúna seasta.
Tábhacht Cosanta Teirmeach
Is féidir le foirceannadh mótair teorainneacha teochta sábháilte a shárú le linn oibriú fada nó coinníollacha ard-ualaigh, rud a fhágann go bhfuil insliú ag dul in aois, damáiste iompair, agus fiú dóite mótair. D’fhéadfadh guaiseacha dóiteáin nó rioscaí sábháilteachta leictreachais a bheith ag baint le róthéamh freisin. Déanann meicníochtaí cosanta teirmeach monatóireacht ar theocht an mhótair i bhfíor-am agus gníomhaíonn siad bearta cosanta nuair is gá, ag cinntiú oibriú iontaofa. I lucht leanúna seasta, ní hamháin go gcosnaíonn cosaint theirmeach an mótar ach feabhsaíonn sé cáilíocht an táirge agus taithí an úsáideora freisin.
Cineálacha Meicníochtaí um Chosaint Theirmeach
Tá anrmal protection in standing fan motors is generally categorized into mechanical and electronic types. Mechanical protection often uses bimetallic strips or thermal switches, which disconnect the circuit based on thermal expansion properties. Electronic protection employs temperature sensors or thermistors (NTC/PTC) to measure temperature, with control circuits determining whether to cut power or reduce load. Electronic protection offers faster response and higher accuracy, enabling multi-level temperature control and fault alarm functions. Mechanical protection is cost-effective and simple, commonly applied in low-power household fans.
Prionsabal Spreagtha um Chosaint Theirmeach
Tá anrmal protection activation is based on temperature detection and threshold judgment. Mechanical switches use thermal expansion to open contacts and disconnect power. Electronic protection converts temperature readings into voltage or resistance signals, allowing control chips to determine whether the motor exceeds preset temperature thresholds. When excessive heat is detected, the system can immediately cut power, reduce speed, or implement intermittent operation. Designers must consider sensor placement, response time, and hysteresis to avoid false triggers and ensure reliable protection.
Paraiméadair Dearaidh Eochracha
I measc na bpríomhpharaiméadair i ndearadh cosanta teirmeach tá tairseacha teochta, am freagartha, modhanna athshocraithe, agus suíomh suiteála. Cinntear luachanna tairsí bunaithe ar chumhacht rátáilte mótair, aicme inslithe, agus timpeallacht oibriúcháin, de ghnáth thart ar 120 ℃ do mhótair lucht leanúna tí. Bíonn tionchar díreach ag am freagartha ar éifeachtúlacht cosanta; seachnaíonn freagra níos tapúla damáiste mótair. I measc na modhanna athshocraithe tá athshocrú uathoibríoch agus láimhe. Oireann athshocrú uathoibríoch d’oibriú leanúnach, agus cuireann athshocrú láimhe le sábháilteacht in iarratais ard-riosca. Ba chóir braiteoirí a chur in aice leis na limistéir foirceannadh nó hotspot chun na teochtaí criticiúla a léiriú go beacht.
Comhordú le Diomailt Teasa
Tá anrmal protection works best when combined with effective heat dissipation. Proper airflow design, installation of heat sinks, and blade arrangement reduce localized motor temperatures, improving protection accuracy. Good heat dissipation delays temperature rise, reducing frequent protective trips and extending motor lifespan. Thermal simulation can evaluate temperature distribution, ensuring the protection device functions at key hotspots.
Breithnithe Iontaofachta agus Fadsaoil
Tá anrmal protection devices in standing fan motors must exhibit high reliability and long operational life. Mechanical switches should withstand multiple thermal cycles without failure, while electronic sensors require high precision and resistance to electrical interference. Selecting high-quality materials, optimizing contact structures, and implementing moisture and dust protection enhance reliability. A robust thermal protection system prevents motor burnout and accidents during long-term use, ensuring product safety.